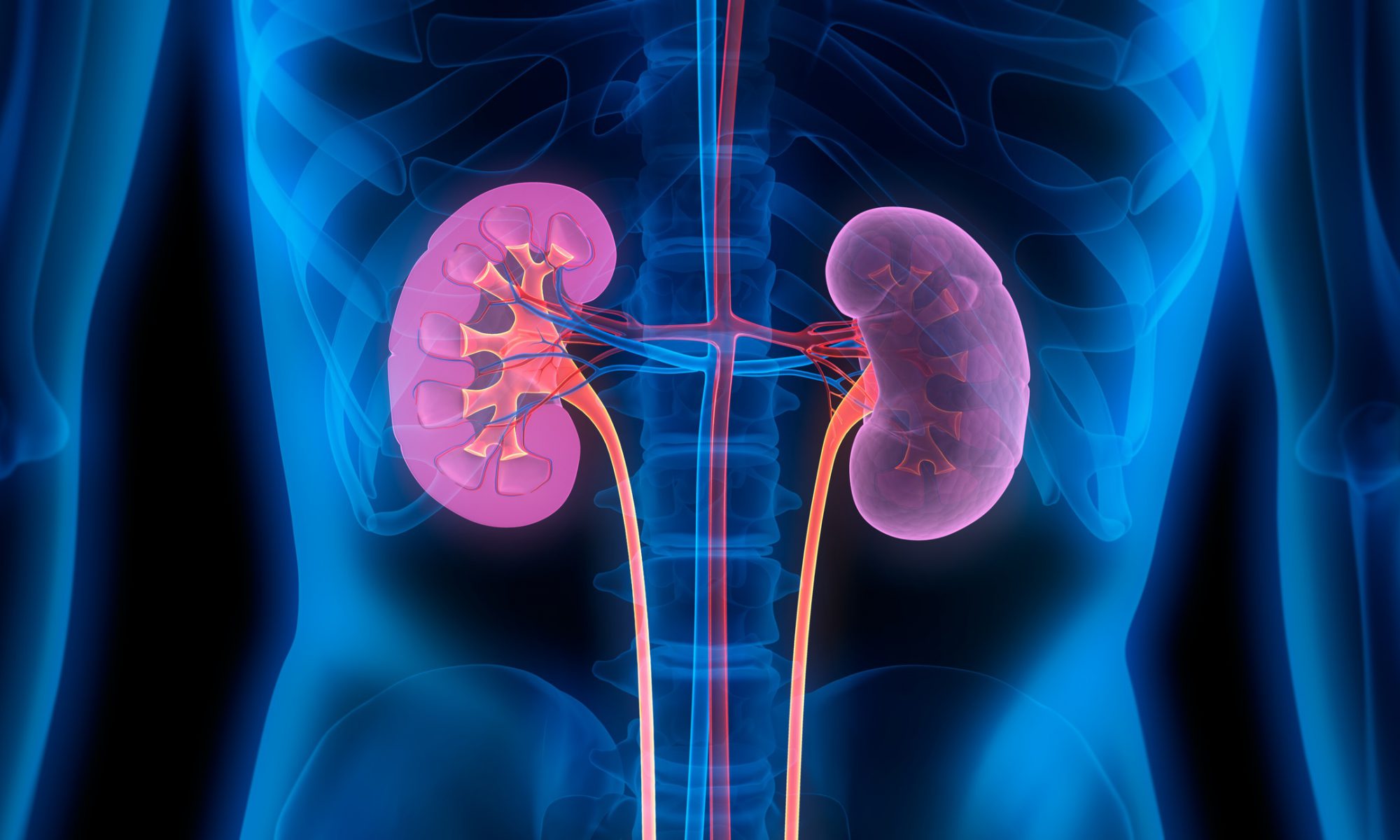
Chronic kidney disease is defined as damage of the renal parenchyma that results in chronic deterioration of kidney function and may result in progression to end-stage renal disease. It is a non-communicable disease that includes a range of physiological disorders which are attributed to abnormal renal function and its progressive decline infiltration rate (the glomerular filtration rate).
There are five stages of kidney damage in chronic kidney disease that range from mild kidney dysfunction to complete failure. The burden of chronic kidney disease is increasing worldwide and is becoming increasingly prevalent in developing countries. Overall, the prevalence is estimated to be between 8 and 16% worldwide. Patients who have stage three or four chronic kidney disease are at a higher risk of progressing to either end-stage renal disease or death. Read more.